Using Multiple Temporal Task Queues
Temporal gives you flexibility to define different task queues to route workflows and activities to specific workers. When a worker starts up, it is configured to consume from a specific task queue by name, along with the activities and workflows it is capable of running.
For example:
import asyncioimport concurrent.futures
from activities import my_good_activityfrom temporalio.client import Clientfrom temporalio.worker import Workerfrom workflows import MyGoodWorkflow
async def main(): client = await Client(...)
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=100) as activity_executor: worker = Worker( client, task_queue="my-task-queue", workflows=[MyGoodWorkflow], activities=[my_good_activity], activity_executor=activity_executor, ) await worker.run()
if __name__ == "__main__": print("Starting worker") asyncio.run(main())Let’s say we wanted to execute the workflows using one task queue and the activities with another. We could write two separate workers, like this.
For workflows:
import asyncioimport concurrent.futures
from temporalio.client import Clientfrom temporalio.worker import Workerfrom workflows import MyGoodWorkflow
async def main(): client = await Client(...)
worker = Worker( client, task_queue="my-workflow-task-queue", workflows=[MyGoodWorkflow], activities=[], ) await worker.run()
if __name__ == "__main__": print("Starting workflow worker") asyncio.run(main())For activities:
import asyncioimport concurrent.futures
from activities import my_good_activityfrom temporalio.client import Clientfrom temporalio.worker import Worker
async def main(): client = await Client(...)
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=100) as activity_executor: worker = Worker( client, task_queue="my-activity-task-queue", workflows=[], activities=[my_good_activity], activity_executor=activity_executor, ) await worker.run()
if __name__ == "__main__": print("Starting activity worker") asyncio.run(main())If we run each of these workers independently
python -m run_workflow_workerpython -m run_activity_workernow we can start a workflow and the two worker processes will execute the workflow and activity code:
import asyncioimport uuid
from temporalio.client import Clientfrom workflows import MyGoodWorkflow, MyWorkflowGoodArgs
async def main(): client = await Client(...)
result = await client.execute_workflow( MyGoodWorkflow.run, MyWorkflowArgs( arg1="good", arg2="workflow", ), id=str(uuid.uuid4()), task_queue="my-workflow-task-queue", )
print(f"Workflow completed with result: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__": asyncio.run(main())If we did it right, when we run a workflow, we can see each task queue show up separately in the Temporal UI.
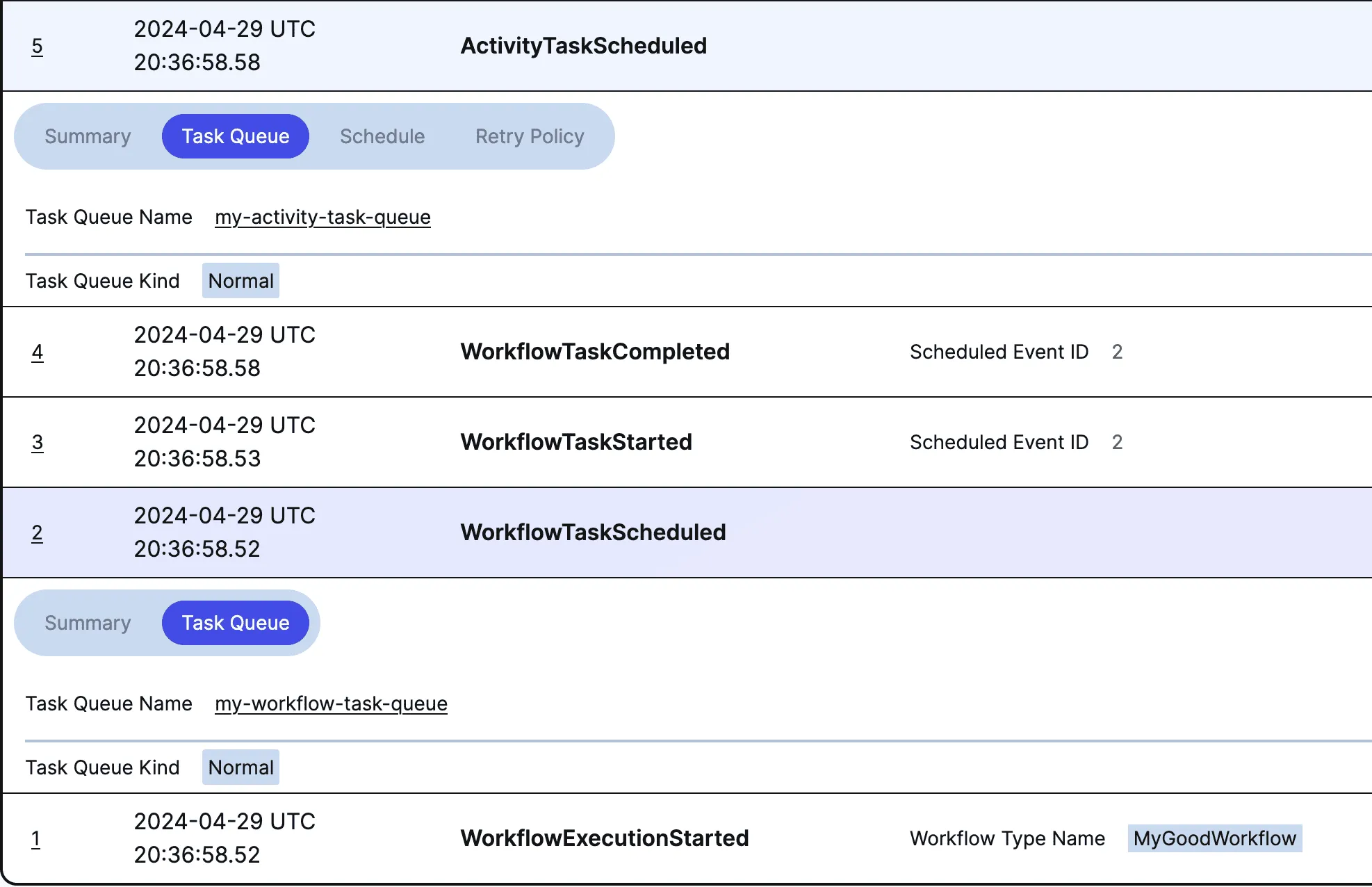
Note: the Temporal samples-python has a multi-language example of this pattern using Python and Go.
Recommended
Temporal Parallel Child Workflows
Temporal provides helpful primitives called Workflows and Activities for orchestrating processes. A common pattern I've found useful is the ability...
Importing Activities for a Temporal Workflow in Python
A spot where I slipped up in trying to adopt Temporal in an existing Python project and then again in starting a new Python project was in defining a...